A tuple is a built-in data collection type. It allows us to store values in a sequence. It is immutable, so no change is reflected in the original data. It uses () brackets rather than [] square brackets to create a tuple. We cannot remove any element but can find in the tuple. We can use indexing to get elements. It also allows traversing elements in reverse order by using negative indexing. Tuple supports various methods like max(), sum(), sorted(), Len() etc.
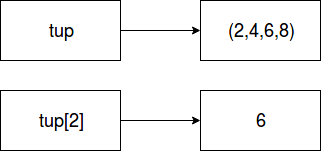
To create a tuple, we can declare it as below.
Example:
- # Declaring tuple
- tup = (2,4,6,8)
- # Displaying value
- print(tup)
- # Displaying Single value
- print(tup[2])
Output:
(2, 4, 6, 8) 6
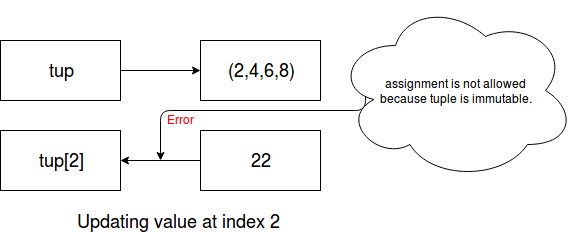
It is immutable. So updating tuple will lead to an error.
Example:
- # Declaring tuple
- tup = (2,4,6,8)
- # Displaying value
- print(tup)
- # Displaying Single value
- print(tup[2])
- # Updating by assigning new value
- tup[2]=22
- # Displaying Single value
- print(tup[2])
Output:
tup[2]=22 TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment (2, 4, 6, 8)