Examples of NFA
Example 1:
Design a NFA for the transition table as given below:
| Present State | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| →q0 | q0, q1 | q0, q2 |
| q1 | q3 | ε |
| q2 | q2, q3 | q3 |
| →q3 | q3 | q3 |
Solution:
The transition diagram can be drawn by using the mapping function as given in the table.
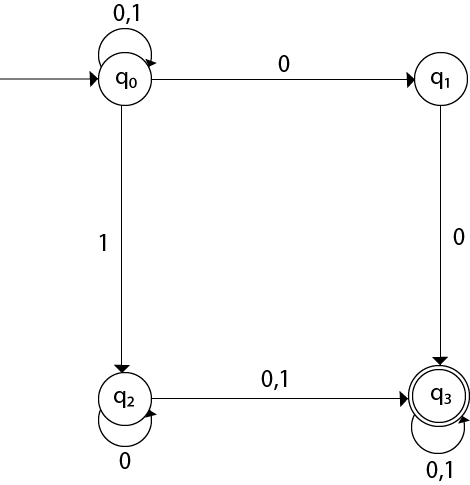
Here,
- δ(q0, 0) = {q0, q1}
- δ(q0, 1) = {q0, q2}
- Then, δ(q1, 0) = {q3}
- Then, δ(q2, 0) = {q2, q3}
- δ(q2, 1) = {q3}
- Then, δ(q3, 0) = {q3}
- δ(q3, 1) = {q3}
Example 2:
Design an NFA with ∑ = {0, 1} accepts all string ending with 01.
Solution:

Hence, NFA would be:
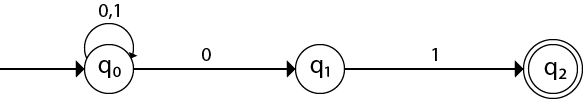
Example 3:
Design an NFA with ∑ = {0, 1} in which double ‘1’ is followed by double ‘0’.
Solution:
The FA with double 1 is as follows:

It should be immediately followed by double 0.
Then,

Now before double 1, there can be any string of 0 and 1. Similarly, after double 0, there can be any string of 0 and 1.
Hence the NFA becomes:
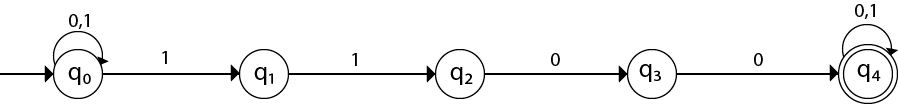
Now considering the string 01100011
- q0 → q1 → q2 → q3 → q4 → q4 → q4 → q4
Example 4:
Design an NFA in which all the string contain a substring 1110.
Solution:
The language consists of all the string containing substring 1010. The partial transition diagram can be:

Now as 1010 could be the substring. Hence we will add the inputs 0’s and 1’s so that the substring 1010 of the language can be maintained. Hence the NFA becomes:
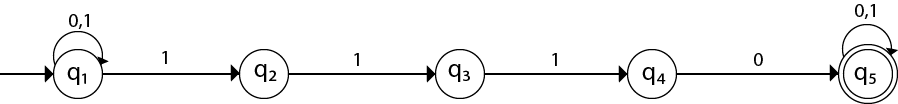
Transition table for the above transition diagram can be given below:
| Present State | 0 | 1 |
|---|---|---|
| →q1 | q1 | q1, q2 |
| q2 | q3 | |
| q3 | q4 | |
| q4 | q5 | |
| *q5 | q5 | q5 |
Consider a string 111010,
- δ(q1, 111010) = δ(q1, 1100)
- = δ(q1, 100)
- = δ(q2, 00)
Got stuck! As there is no path from q2 for input symbol 0. We can process string 111010 in another way.
- δ(q1, 111010) = δ(q2, 1100)
- = δ(q3, 100)
- = δ(q4, 00)
- = δ(q5, 0)
- = δ(q5, ε)
As state q5 is the accept state. We get the complete scanned, and we reached to the final state.
Example 5:
Design an NFA with ∑ = {0, 1} accepts all string in which the third symbol from the right end is always 0.
Solution:
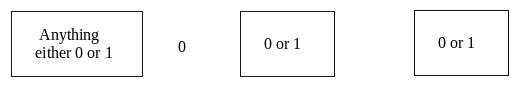
Thus we get the third symbol from the right end as ‘0’ always. The NFA can be:
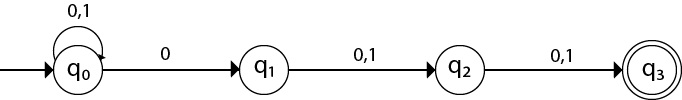
The above image is an NFA because in state q0 with input 0, we can either go to state q0 or q1.
- Theory of Automata
- Finite Automata
- Transition Diagram
- Transition Table
- DFA (Deterministic finite automata)
- Examples of DFA
- NFA (Non-Deterministic finite automata)
- Examples of NFA
- Eliminating ε Transitions
- Conversion from NFA to DFA
- Conversion from NFA with ε to DFA
- Minimization of DFA
- Regular Expression
- Examples of Regular Expression
- Moore Machine
- Mealy Machine
- Context Free Grammar
- Simplification of CFG
- Chomsky’s Normal Form (CNF)
- Greibach Normal Form (GNF)
- Pushdown Automata(PDA)
- Non-deterministic Pushdown Automata
- Turing Machine
- Examples of TM

