Transition Table
The transition table is basically a tabular representation of the transition function. It takes two arguments (a state and a symbol) and returns a state (the “next state”).
A transition table is represented by the following things:
- Columns correspond to input symbols.
- Rows correspond to states.
- Entries correspond to the next state.
- The start state is denoted by an arrow with no source.
- The accept state is denoted by a star.
Example 1:
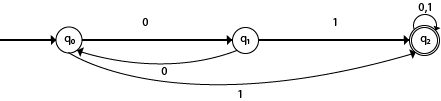
Solution:
Transition table of given DFA is as follows
| Present State | Next state for Input 0 | Next State of Input 1 |
|---|---|---|
| →q0 | q1 | q2 |
| q1 | q0 | q2 |
| *q2 | q2 | q2 |
Explanation:
- In the above table, the first column indicates all the current states. Under column 0 and 1, the next states are shown.
- The first row of the transition table can be read as, when the current state is q0, on input 0 the next state will be q1 and on input 1 the next state will be q2.
- In the second row, when the current state is q1, on input 0, the next state will be q0, and on 1 input the next state will be q2.
- In the third row, when the current state is q2 on input 0, the next state will be q2, and on 1 input the next state will be q2.
- The arrow marked to q0 indicates that it is a start state and circle marked to q2 indicates that it is a final state.
Example 2:
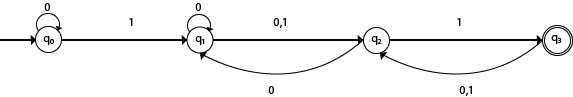
Solution:
Transition table of given NFA is as follows:
| Present State | Next state for Input 0 | Next State of Input 1 |
|---|---|---|
| →q0 | q0 | q1 |
| q1 | q1, q2 | q2 |
| q2 | q1 | q3 |
| *q3 | q2 | q2 |
Explanation:
- The first row of the transition table can be read as, when the current state is q0, on input 0 the next state will be q0 and on input 1 the next state will be q1.
- In the second row, when the current state is q1, on input 0 the next state will be either q1 or q2, and on 1 input the next state will be q2.
- In the third row, when the current state is q2 on input 0, the next state will be q1, and on 1 input the next state will be q3.
- In the fourth row, when the current state is q3 on input 0, the next state will be q2, and on 1 input the next state will be q2.
- Theory of Automata
- Finite Automata
- Transition Diagram
- Transition Table
- DFA (Deterministic finite automata)
- Examples of DFA
- NFA (Non-Deterministic finite automata)
- Examples of NFA
- Eliminating ε Transitions
- Conversion from NFA to DFA
- Conversion from NFA with ε to DFA
- Minimization of DFA
- Regular Expression
- Examples of Regular Expression
- Moore Machine
- Mealy Machine
- Context Free Grammar
- Simplification of CFG
- Chomsky’s Normal Form (CNF)
- Greibach Normal Form (GNF)
- Pushdown Automata(PDA)
- Non-deterministic Pushdown Automata
- Turing Machine
- Examples of TM
Post Views: 651

