- NFA stands for non-deterministic finite automata. It is easy to construct an NFA than DFA for a given regular language.
- The finite automata are called NFA when there exist many paths for specific input from the current state to the next state.
- Every NFA is not DFA, but each NFA can be translated into DFA.
- NFA is defined in the same way as DFA but with the following two exceptions, it contains multiple next states, and it contains ε transition.
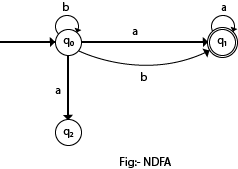
In the following image, we can see that from state q0 for input a, there are two next states q1 and q2, similarly, from q0 for input b, the next states are q0 and q1. Thus it is not fixed or determined that with a particular input where to go next. Hence this FA is called non-deterministic finite automata.
Formal definition of NFA:
NFA also has five states same as DFA, but with different transition function, as shown follows:
δ: Q x ∑ →2Q
where,
- Q: finite set of states
- ∑: finite set of the input symbol
- q0: initial state
- F: final state
- δ: Transition function
Graphical Representation of an NFA
The state is represented by vertices.
- The arc labeled with an input character show the transitions.
- The initial state is marked with an arrow.
- The final state is denoted by the double circle.
Example 1:
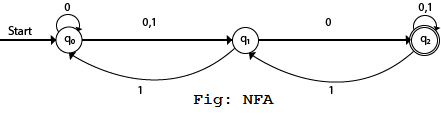
- Q = {q0, q1, q2}
- ∑ = {0, 1}
- q0 = {q0}
- F = {q2}
Solution:
Transition diagram:
Transition Table:
| Present State | Next state for Input 0 | Next State of Input 1 |
|---|---|---|
| →q0 | q0, q1 | q1 |
| q1 | q2 | q0 |
| *q2 | q2 | q1, q2 |
In the above diagram, we can see that when the current state is q0, on input 0, the next state will be q0 or q1, and on 1 input the next state will be q1. When the current state is q1, on input 0 the next state will be q2 and on 1 input, the next state will be q0. When the current state is q2, on 0 input the next state is q2, and on 1 input the next state will be q1 or q2.
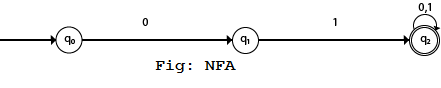
Example 2:
NFA with ∑ = {0, 1} accepts all strings with 01.
Solution:
Transition Table:
| Present State | Next state for Input 0 | Next State of Input 1 |
|---|---|---|
| →q0 | q1 | ε |
| q1 | ε | q2 |
| *q2 | q2 | q2 |
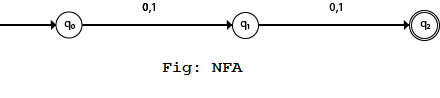
Example 3:
NFA with ∑ = {0, 1} and accept all string of length atleast 2.
Solution:
Transition Table:
| Present State | Next state for Input 0 | Next State of Input 1 |
|---|---|---|
| →q0 | q1 | q1 |
| q1 | q2 | q2 |
| *q2 | ε | ε |
- Theory of Automata
- Finite Automata
- Transition Diagram
- Transition Table
- DFA (Deterministic finite automata)
- Examples of DFA
- NFA (Non-Deterministic finite automata)
- Examples of NFA
- Eliminating ε Transitions
- Conversion from NFA to DFA
- Conversion from NFA with ε to DFA
- Minimization of DFA
- Regular Expression
- Examples of Regular Expression
- Moore Machine
- Mealy Machine
- Context Free Grammar
- Simplification of CFG
- Chomsky’s Normal Form (CNF)
- Greibach Normal Form (GNF)
- Pushdown Automata(PDA)
- Non-deterministic Pushdown Automata
- Turing Machine
- Examples of TM

