Design FA with ∑ = {0, 1} accepts even number of 0’s and even number of 1’s.
Solution:
This FA will consider four different stages for input 0 and input 1. The stages could be:
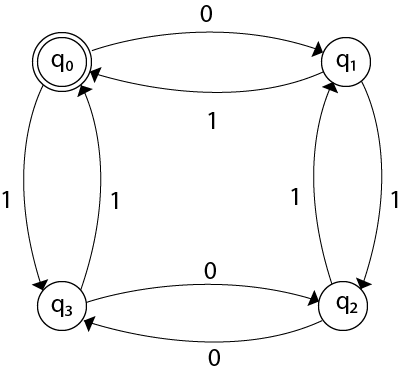
Here q0 is a start state and the final state also. Note carefully that a symmetry of 0’s and 1’s is maintained. We can associate meanings to each state as:
q0: state of even number of 0’s and even number of 1’s.
q1: state of odd number of 0’s and even number of 1’s.
q2: state of odd number of 0’s and odd number of 1’s.
q3: state of even number of 0’s and odd number of 1’s.
Example 4:
Design FA with ∑ = {0, 1} accepts the set of all strings with three consecutive 0’s.
Solution:
The strings that will be generated for this particular languages are 000, 0001, 1000, 10001, …. in which 0 always appears in a clump of 3. The transition graph is as follows:
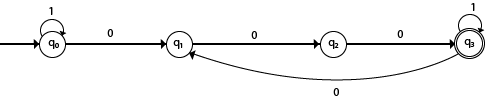
Note that the sequence of triple zeros is maintained to reach the final state.
Example 5:
Design a DFA L(M) = {w | w ε {0, 1}*} and W is a string that does not contain consecutive 1’s.
Solution:
When three consecutive 1’s occur the DFA will be:
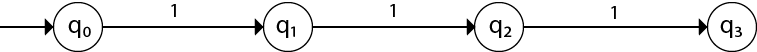
Here two consecutive 1’s or single 1 is acceptable, hence
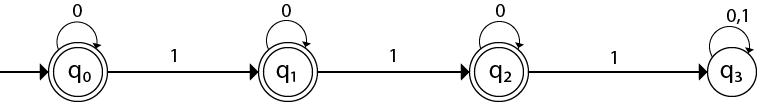
The stages q0, q1, q2 are the final states. The DFA will generate the strings that do not contain consecutive 1’s like 10, 110, 101,….. etc.
Example 6:
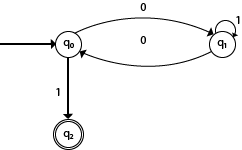
Design a FA with ∑ = {0, 1} accepts the strings with an even number of 0’s followed by single 1.
Solution:
The DFA can be shown by a transition diagram as:
- Theory of Automata
- Finite Automata
- Transition Diagram
- Transition Table
- DFA (Deterministic finite automata)
- Examples of DFA
- NFA (Non-Deterministic finite automata)
- Examples of NFA
- Eliminating ε Transitions
- Conversion from NFA to DFA
- Conversion from NFA with ε to DFA
- Minimization of DFA
- Regular Expression
- Examples of Regular Expression
- Moore Machine
- Mealy Machine
- Context Free Grammar
- Simplification of CFG
- Chomsky’s Normal Form (CNF)
- Greibach Normal Form (GNF)
- Pushdown Automata(PDA)
- Non-deterministic Pushdown Automata
- Turing Machine
- Examples of TM


